Material
Abstract
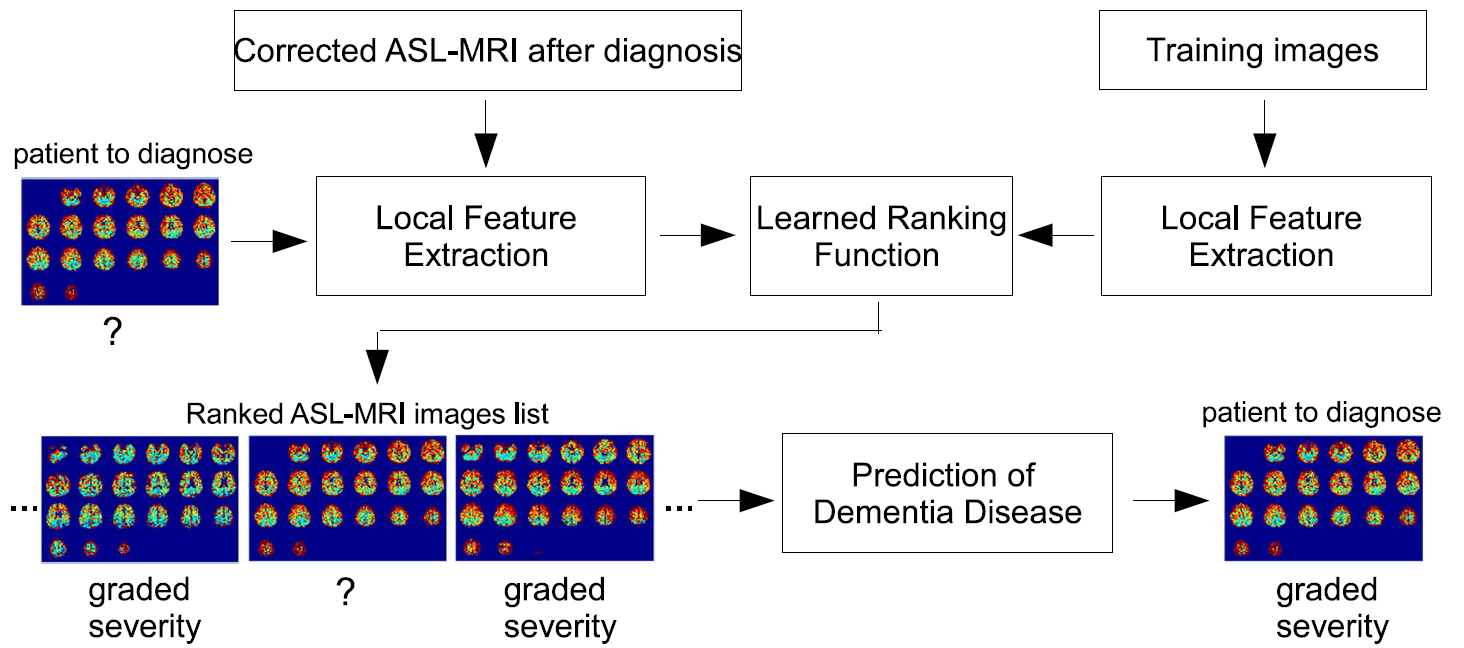
Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) is an emerging magnetic resonance imaging technique attracting increasing attention in dementia diagnosis only beginning from recent years. ASL is capable to provide direct and quantitative measurement of cerebral blood flow (CBF) of scanned patients, so that brain atrophy of demented patients could be revealed by measured low CBF within certain brain regions through ASL. However, partial volume effects (PVE) mainly caused by signal cross-contamination due to pixel heterogeneity and limited spatial resolution of ASL, often prevents CBF from being precisely measured. Inaccurate CBF is prone to mislead and even deteriorate dementia disease diagnosis results, thereafter. In this paper, a novel dementia disease diagnosis strategy based on ASL is proposed for the first time. The diagnosis strategy is composed of two steps: 1) to conduct pixel-wise PVE correction on original ASL images and 2) to predict dementia disease severities based on corrected ASL images via ranking. Extensive experiments and comprehensive statistical analysis are carried out to demonstrate the superiority of the new strategy with comparison to several existing ones. Promising results are reported from the statistical point of view.